Neural Tourniquet

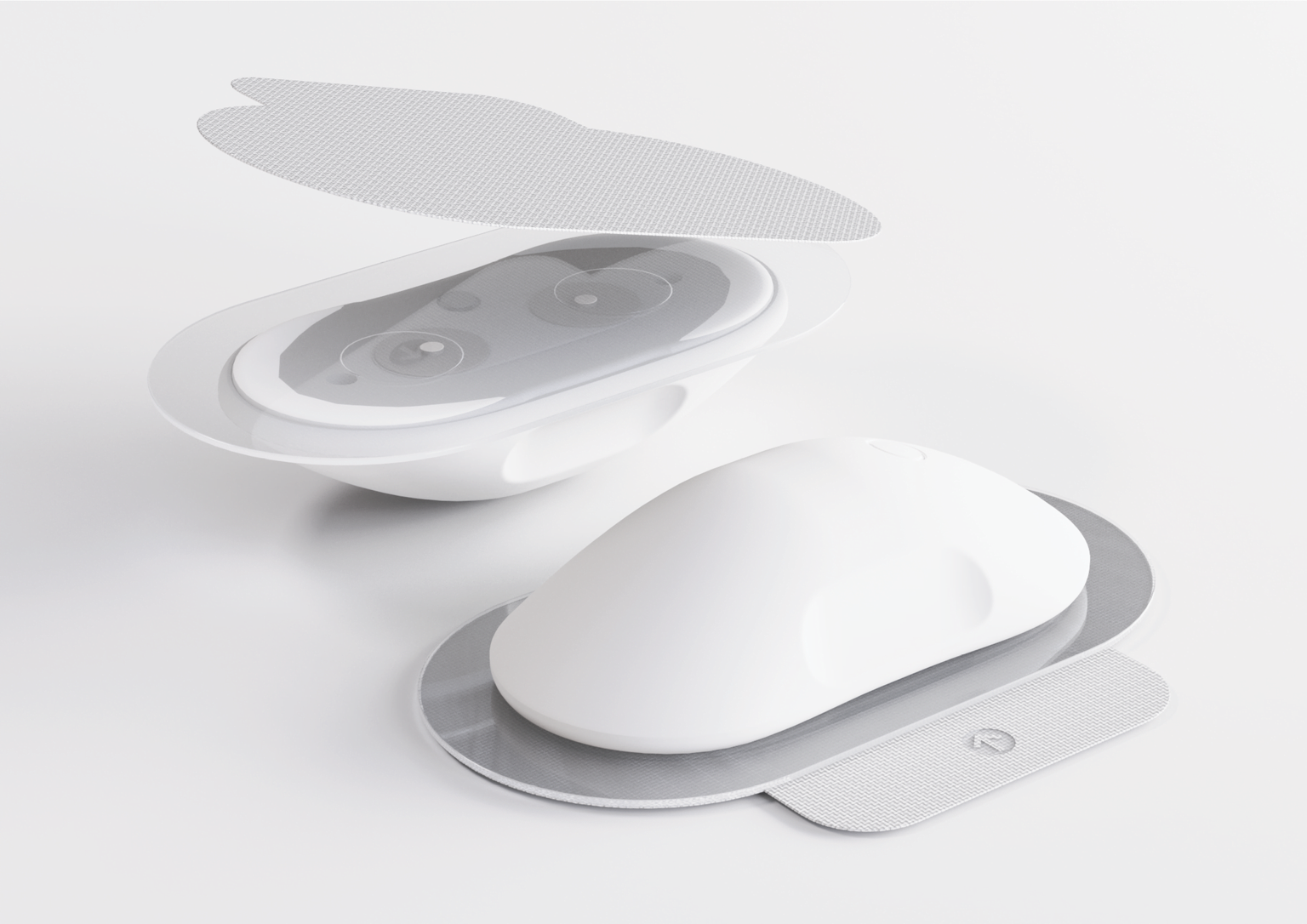
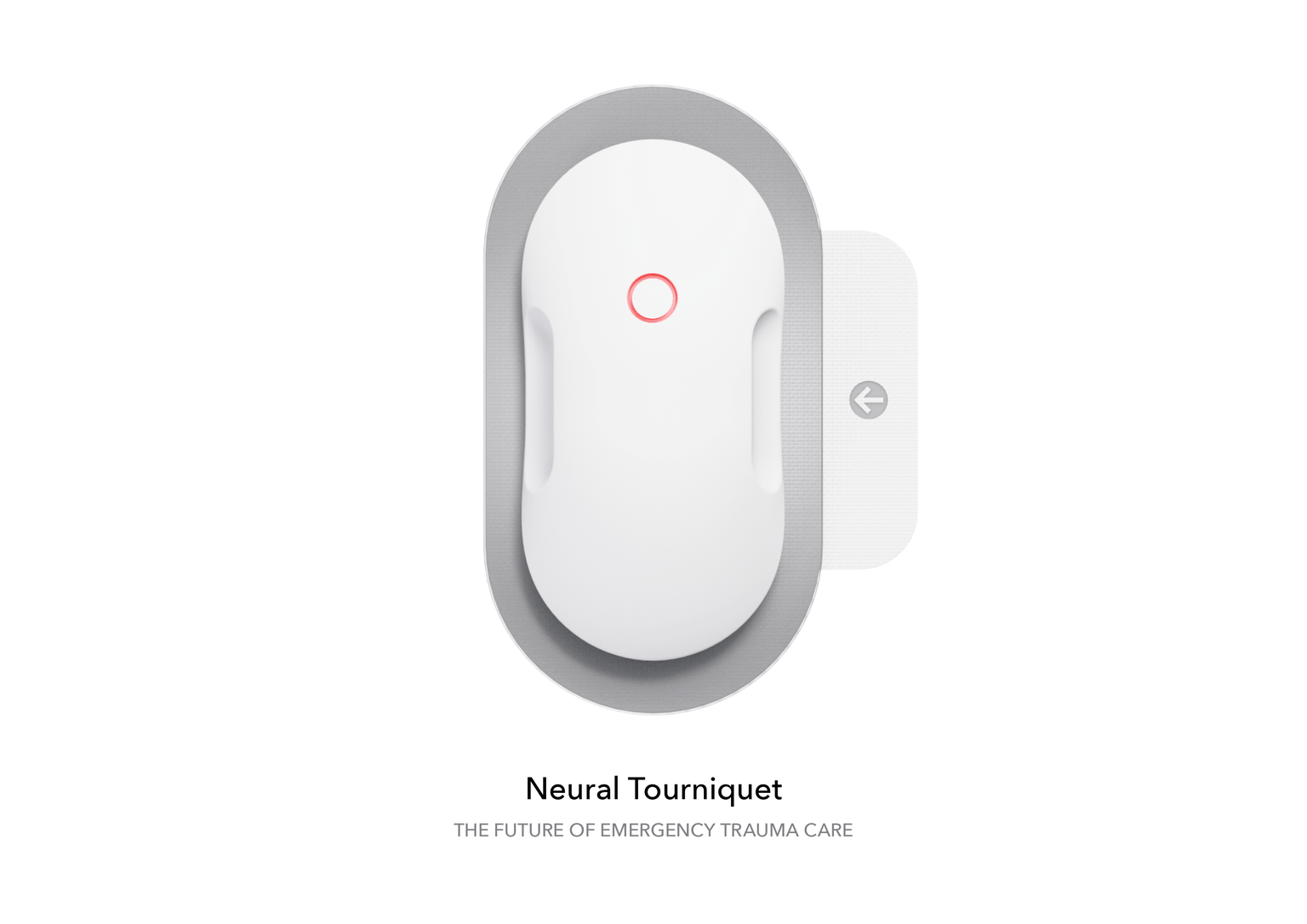
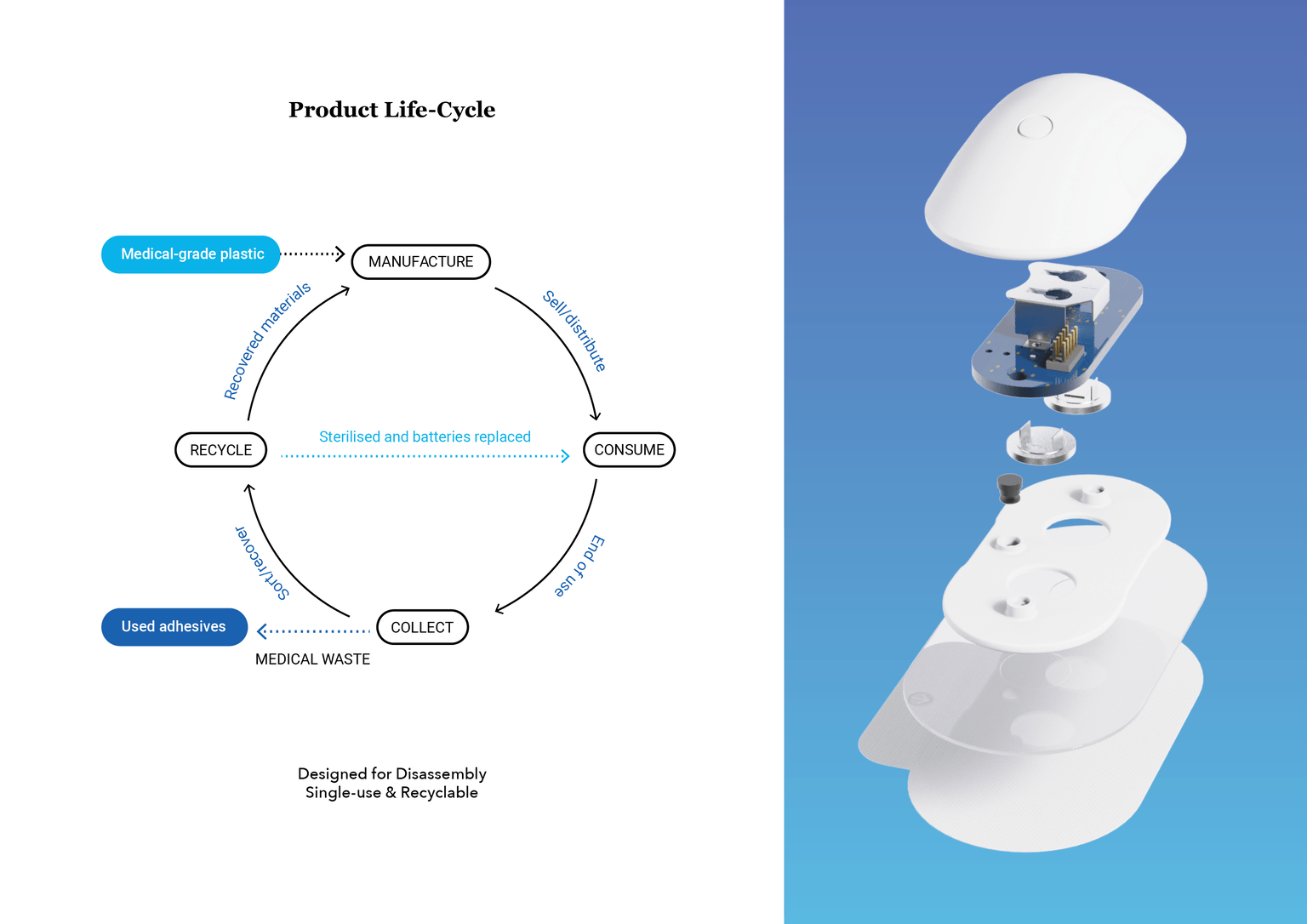
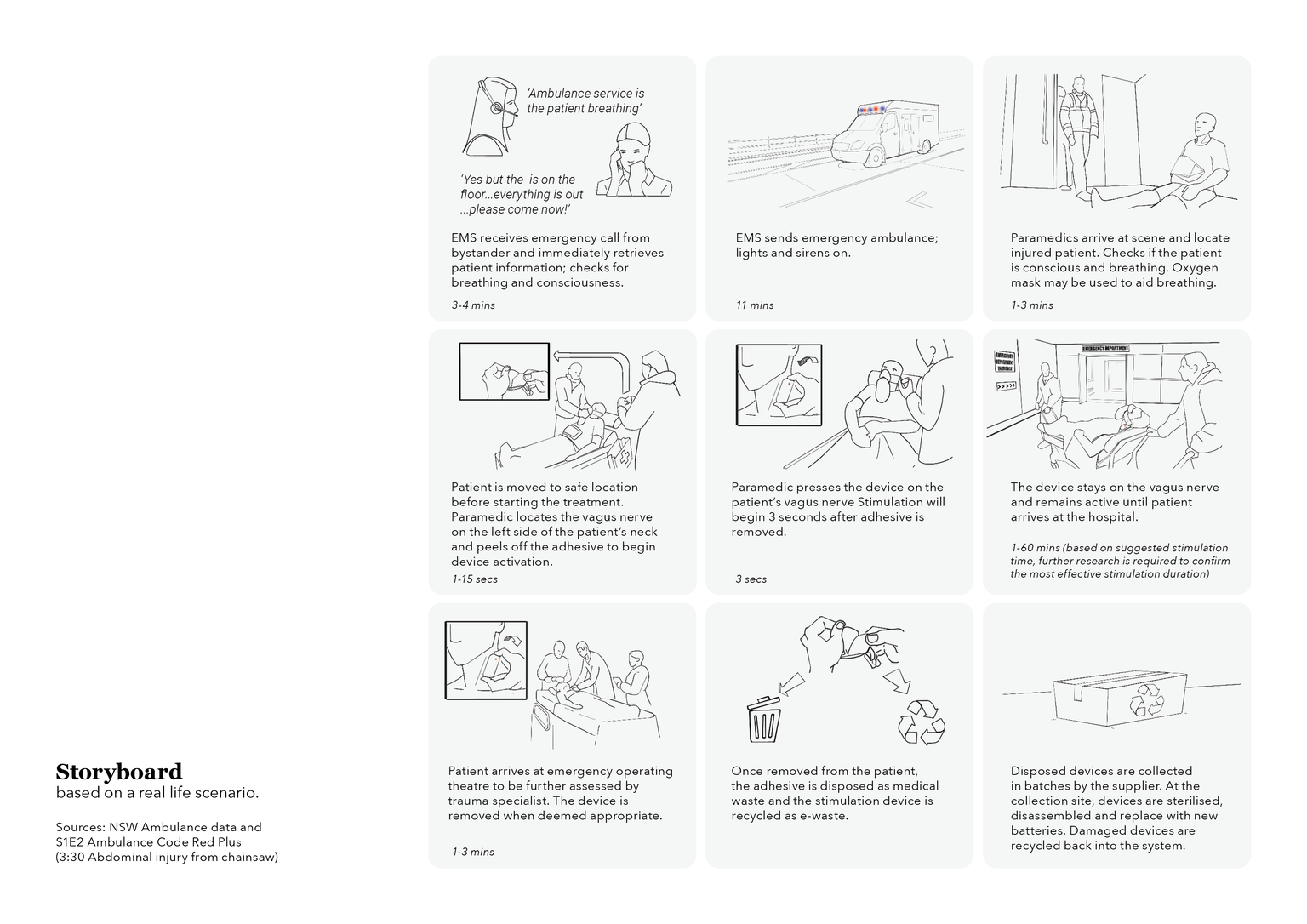
The Neural Tourniquet is designed for paramedics to use in emergency situations where rapid bleeding control is required to save lives in the critical minutes following a traumatic injury. The device uses TENS technology to stimulate the cervical vagus nerve, proven to stop uncontrollable bleeding in under a minute.